What is a Logical Data Warehouse?
Are you having trouble managing and making the most of your data? If the answer is yes, I have good and bad news for you.
The good news is that you are not alone—we’re all struggling to find our way through heaps of data.
The bad news is that it will only get worse: We will be generating 175 zettabytes of data in 2025 according to IDC, which is almost 50 percent more than the total amount of data created in 2022, which was 120 zettabytes. The fact that more than 80 percent of this amount will be unstructured data will make things even more difficult.
So, we need to find new ways of storing, managing, unifying, and consuming our data. We are up against some serious data management challenges, though:
-
Our data is scattered over multiple geographic locations hosting data storage.
-
Different business units use different—and sometimes incompatible—technologies.
-
Decisions like who is responsible for data and who gets to access it further complicate the issue of data integration.
Managing scattered data is expensive; time-sensitive operations demand real-time data; and we must ensure that data is timely, accurate, reliable, discoverable, and accessible. Thankfully, smart people all around the world are working to solve these problems and coming up with creative concepts. Of these concepts, data mesh and data fabric has become quite popular in the last couple of years, as demonstrated by this graph below:
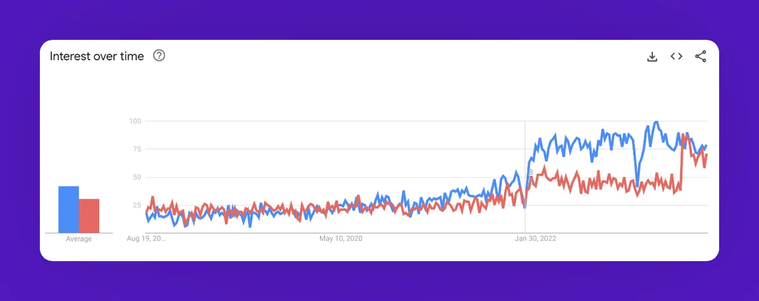
Graph showing the increase in the global Google searches for the terms "data mesh" (blue) and "data fabric" (orange) in the last five years. Image credits: Google Trends. The image was slightly modified for aesthetic purposes.
Underpinning all these ideas is the concept of Logical Data Warehouse (LDW). Although Bill Inmon is credited with coining the term in 2004, it was Mark Beyer of Gartner who used it in 2009 in the sense that it is used today. We’ll take a closer look at the LDW architecture and what it promises to enterprise users in this blog post.
Logical Data Warehouse—what does it do?
An LDW is a data architecture specifically designed to overcome the geographic, technological, and data ownership constraints cited above. This architectural layer is built on top of data warehouses and data lakes in this concept. It harmonizes different components within the data infrastructure to create a single, integrated view of the data scattered across different storage locations. While achieving this feat, LDW makes no use of physical ELT and ETL processes generally used to copy and move data into a single storage.
Key takeaways
-
An LDW is a composable data architecture that unifies data stored in different locations.
-
The LDW takes advantage of the data virtualization technique to unify data without copying or moving it.
-
The LDW makes it easier for domain experts to bring together their data without relying on an IT department since there is no need for ETL or ELT processes involved.
-
The LDW lends itself to the SaaS-heavy work environment where pulling in data from various SaaS tools is key.
Data in numbers
-
The latest estimates put the amount of data being created every day at 328.77 million terabytes.
-
The global data storage market, valued at $217.02 billion in 2022, is expected to reach $777.98 billion in 2030.
-
The demand for data scientists won’t slow down any time soon. The number of data scientist jobs is expected to increase by 36 percent from 2021 to 2031, with 13,500 job openings on average every year throughout the decade.
-
41 percent of C-suite executives consider metadata and governance as the biggest challenges, while 31 percent are concerned about slow data ingestion.
How does an LDW work?
How does an LDW manage to bring together all the data regardless of its format when the user has no idea where the data resides? The power of the LDW architecture lies in how it can capitalize on metadata. An LDW does not physically house data but holds metadata that defines the context of data, making it possible for data consumers to find and access a specific piece of data without having to know where it is stored. Metadata eliminates the need to perform ETL processes or replicate data and presents the users with a unified view of data upon a simple information request they send.
The data needs of a modern enterprise are so sophisticated that no single data management system can address the demands of all user types and use cases. The LDW offers an all-encompassing, versatile, and flexible model that can do that by utilizing data warehouses, data lakes, Hadoop clusters, NoSQL databases, or cloud-based platforms. Different components work in sync within an LDW framework to handle structured or unstructured data, and relational or non-relational databases. The result can approximate real-time or provide a single view of truth with data historicity, depending on what the user seeks. Imagine two hypothetical data consumers: One prioritizing data quality over access speed and another who doesn't have high standards for data consistency while showing no tolerance for latency. The LDW can lean on different components to satisfy both.
Comparison: Strengths and weaknesses of the LDW
-
An LDW lowers the technical barriers for knowledge workers or "domain experts," practically turning them into "citizen data analysts." These people can self-serve without having to execute physical ELT and ETL processes. An LDW architecture empowers them to find and access data without relying on an already-overwhelmed IT department.
-
The centralized data source built by an LDW minimizes the need for data movement and replication. This prevents data sprawl and degradation, improving data governance.
-
An LDW architecture allows for data historicity, the lack of which was a weak point for data virtualization, as our CEO Mustafa explained earlier. The LDW can harness the capabilities of a Hadoop cluster to provide users with historical analysis. Coupled with real-time or near-real-time data analysis, it offers users the best of both worlds.
-
The flexibility an LDW architecture affords its users is immense compared to conventional enterprise data warehouses. The LDW represents a composable architecture. New components can be added and removed with ease, which is a huge plus in an age where people use multiple SaaS products and have difficulty integrating them into the existing data infrastructure. An LDW removes the need to establish new ELT and ETL processes every time a new data source is added to an existing data infrastructure.
An LDW architecture is not without its weaknesses. Those weaknesses follow directly from data virtualization, which is the technique it utilizes for implementation. Luckily, we have the caching to mitigate the scalability problems. Additionally, different components of the architecture being down renders data analysis temporarily inaccessible. This is a problem that takes a holistic maintenance approach to deal with, as is the case with data virtualization.
How does the LDW fit with data virtualization, data mesh, and data fabric?
-
Data virtualization is a specific data integration technique to realize the LDW principles. It is what an LDW uses to bring together disparate sources of data without copying or moving the data.
-
Data mesh is an approach that redefines how we think about data. It is basically a mental exercise in developing a novel way of focusing on knowledge domains, treating data as a product, and prioritizing the empowerment of knowledge workers. The data mesh concept leverages the LDW to transform the existing data infrastructure in a way that can accommodate the needs of a modern enterprise.
-
Data fabric is defined by Gartner as "an emerging data management design,... not one single tool or technology." It is based on active metadata practices incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Thanks to AI and ML, data fabric can learn patterns of data usage and better service information requests over time. Data fabric is an end state for an LDW to reach once it matures.
What about artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)?
It is unthinkable to wrap up a post without making a reference to AI and ML nowadays. A partnership between the LDW, on the one hand, and AI and ML, on the other, promises to deliver lasting advantages. According to Mayank Talwar, an analyst at Gartner, AI and Logical Data Warehouse are complementary technologies (“Adopting a Logical Data Warehouse,” September 17, 2021, pp. 19-21). Talwar gives us a glimpse into a few scenarios where these two can create synergies:
-
While AI allows the LDW to better understand the data structure and metadata and helps with workload management, the LDW provides the robust infrastructure AI and ML need to deliver the results.
-
Users of an LDW architecture stand to benefit from the analytical tools and methods AI and ML can offer. In return, the LDW generates high-quality data that AI and ML algorithms can train on.
Let’s take a deep dive and see how these two technologies make each other better:
How AI/ML helps LDW
1. Smart query optimization
By analyzing query patterns, AI/ML models predict frequently accessed data, recommend query rewrites, and dynamically optimize query execution paths. As a result, users enjoy shorter query response times and minimal resource consumption.
2. Automated data integration
AI/ML streamlines data integration by classifying and mapping incoming datasets through schema matching and entity resolution and automating ETL/ELT tasks. This accelerates data onboarding, reducing time-to-insight.
3. Metadata and semantic enrichment
AI identifies data relationships and hierarchies, helping users make sense of data and enhancing metadata as a result.
4. Intelligent data virtualization
ML models can help optimize source selection and data routing and analyze usage patterns to determine whether to retrieve live data or use cached data. This brings about enhanced performance and lower costs in federated queries across heterogeneous sources.
5. Anomaly detection and data quality monitoring
Users can leverage AI/ML to monitor data streams for anomalies and sift through large datasets to identify data quality issues. This ensures that data consumers are fed reliable data.
How LDW helps AI/ML
1. Unified access to scattered data
LDWs eliminate the need to physically move data from the data integration process, virtualizing access to disparate data sources. This allows AI/ML to train on more diverse datasets.
2. Faster data availability for model training
LDWs facilitate real-time data integration, which lets ML models train on up-to-date data.
3. Contextual data enrichment
LDWs are used with semantic layers and metadata catalogs, helping users better interpret data. This improves data discoverability and facilitates self-service analytics for business teams.
Conclusion
The LDW is a data architecture modern enterprises should aspire to have. It does not replace the existing enterprise data warehouse but complements it with new components, turning the latter into one of the cogs in a well-oiled machine and reducing the cost of data management. It is the current best practice in data management right now. At least until the next concept with an even cooler name emerges, that is.



 Please
fill out this field
Please
fill out this field









